AACR 2022 Poster 3371
Impact of RNA Degradation on Transcriptomic Profiling in Tumor Samples from Syngeneic Mouse Models
Yanghui Sheng, Wubin Qian, Xiaobo Chen, Henry Q. Li, Sheng Guo
Crown Bioscience, Inc., 218 Xinghu Street, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215000, China
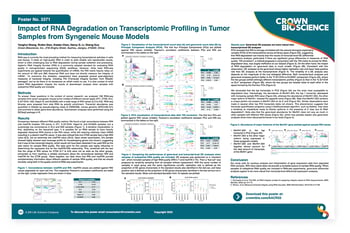 RNA-seq is currently the most prevailing method for measuring transcriptional activities in cells and tissues. It relies on high-quality RNA in order to yield reliable and reproducible results, which is often challenging due to RNA degradation during sample collection and processing. Agilent’s RNA Integrity Number (RIN) is a commonly adopted standard for evaluating RNA quality in next-generation sequencing (NGS) workflows.
RNA-seq is currently the most prevailing method for measuring transcriptional activities in cells and tissues. It relies on high-quality RNA in order to yield reliable and reproducible results, which is often challenging due to RNA degradation during sample collection and processing. Agilent’s RNA Integrity Number (RIN) is a commonly adopted standard for evaluating RNA quality in next-generation sequencing (NGS) workflows.
However, while most RNA-seq experiments are geared towards the quantification of mRNA, the RIN metric heavily relies on the amount of 18S and 28S ribosomal RNA and does not directly measure the integrity of mRNA1. To overcome this limitation, researchers have proposed several post-alignment measures of transcript integrity, including TIN (Transcript Integrity Number, from RSeQC package)2, but so far there is no consensus on which metric to use. It is also unclear to what extent RNA degradation impacts the results of downstream analysis when samples with suboptimal RNA quality are included.
Download this Poster to Discover:
- Need for cautious analysis and interpretation of gene expression data from degraded RNA samples.
- How RIN value alone does not provide a complete picture of sample RNA quality.
- Gene-level differential analyses appear to be more robust than transcript-level differential expression analyses.
Download the Poster Now!

 RNA-seq is currently the most prevailing method for measuring transcriptional activities in cells and tissues. It relies on high-quality RNA in order to yield reliable and reproducible results, which is often challenging due to RNA degradation during sample collection and processing. Agilent’s RNA Integrity Number (RIN) is a commonly adopted standard for evaluating RNA quality in next-generation sequencing (NGS) workflows.
RNA-seq is currently the most prevailing method for measuring transcriptional activities in cells and tissues. It relies on high-quality RNA in order to yield reliable and reproducible results, which is often challenging due to RNA degradation during sample collection and processing. Agilent’s RNA Integrity Number (RIN) is a commonly adopted standard for evaluating RNA quality in next-generation sequencing (NGS) workflows. 
