- Services
- Therapeutic Areas
- Model Systems
- In Vitro
- In Vivo
- Technologies
- Service Type
- About Us
- Our Science
- Start Your Study Now
Wubin Qian, Jia Xue, Henry Q. Li, and Sheng Guo 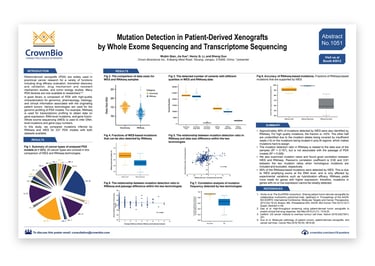
Patient-derived xenografts (PDX) are widely used, highly predictive, preclinical oncology models, useful for a range of study types including drug efficacy evaluation, biomarker discovery and validation, drug mechanism and resistant mechanism studies, and tumor biology studies.
A good quality, well characterized PDX library should include genomic, pharmacology, and histology data, as well as clinical information associated with the original patient tumors. Various technologies are used for PDX genomic profiling e.g. RNAseq to obtain gene expression, RNA-level mutation, and gene fusion data, and whole exome sequencing (WES) for inferring DNA-level mutations and gene copy numbers.
This poster compares PDX mutations inferred by RNAseq and WES for a panel of over 230 models, covering 20 cancer types.
Your privacy is important to us.
We'll never share your information.
© 2024 Crown Bioscience. All Rights Reserved.


© 2024 Crown Bioscience. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy
2023-05-22
2021-10-27
landing_page
PDX/Databases